George Crawford, MD
Laparoscopic Appendectomy
Procedure Overview
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove the vermiform appendix.
INDICATIONS:
- Appendicitis (Acute, Chronic, Gangrenous, Perforated, Suspected, or Uncomplicated)
- Incidental (during another procedure often due to injury or abnormal anatomy)
- Carcinoid tumors (in children and when confined to the tip of the appendix)
- Adenocarcinoma of the appendix requires a right colectomy

Pre-operative Patient Care
Typical recommendations for pre-operative care may include, but are not limited to, any of the following:
- CT Scan with PO or IV contrast.
- Ultrasound in pediatric population.
- Clinical Exam is often enough with a thorough history to make diagnosis.
- Cardiopulmonary evaluation as needed.
- Anesthesiology consultation as needed.
- Nothing by mouth for 6 hours before surgery.
- Prophylactic antibiotics for patients with acute appendicitis.
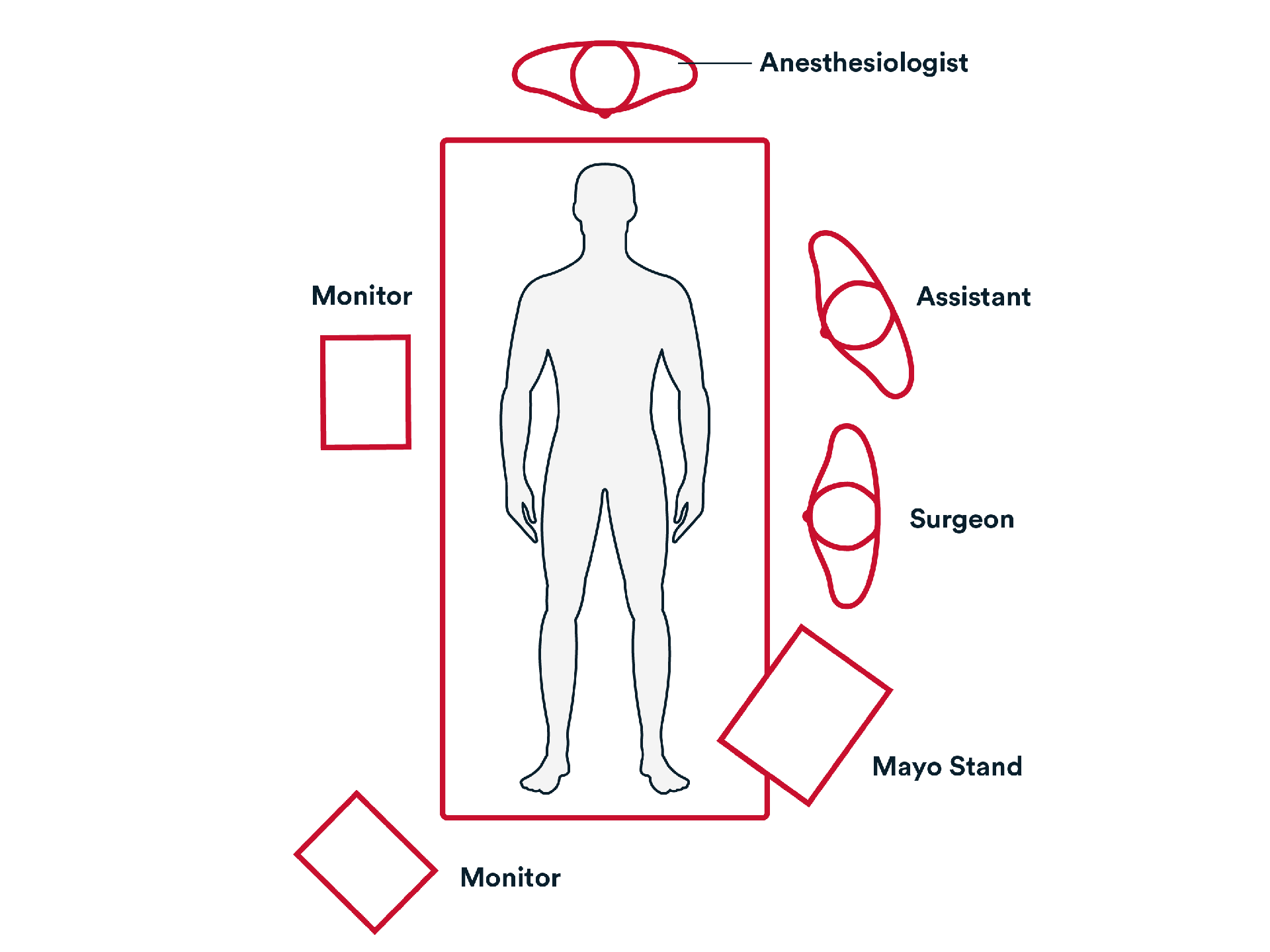
Prep & Patient Positioning
Common patient positioning:
- The patient is supine with both arms tucked at the sides. The operating surgeon and assistant stand on the patient's left.
Placing the patient with the left side down aids gravity in relocating the small bowel away from the appendiceal/cecal field of vision.
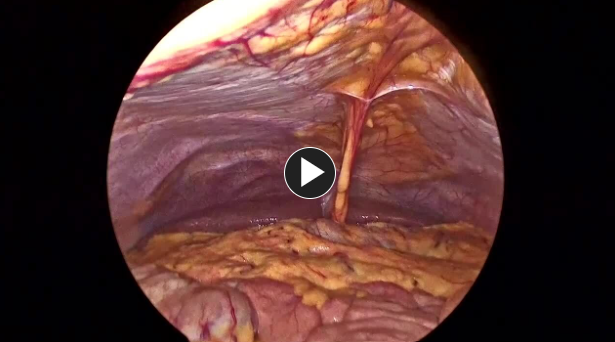
Operative Steps
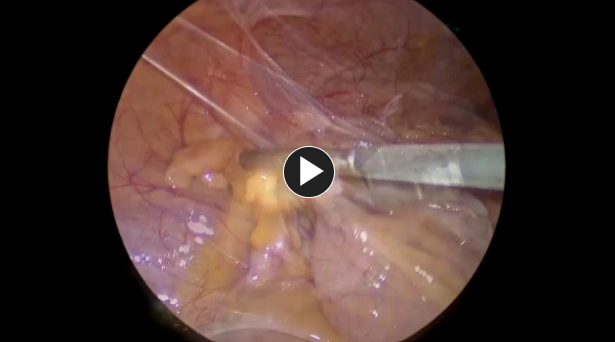
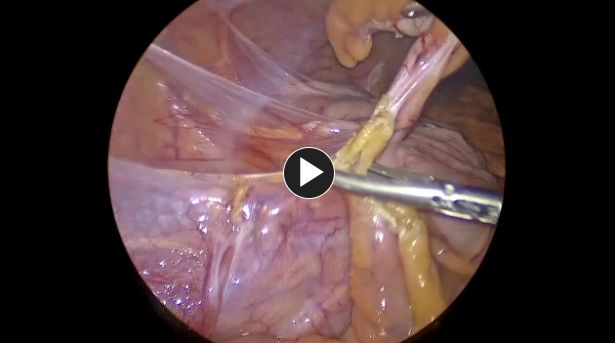
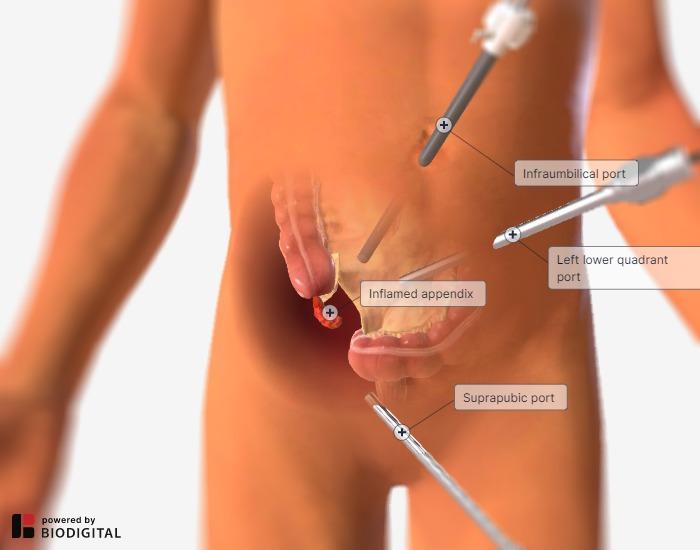
1. Access
- Patient is positioned, prepped, and draped. Access is generally obtained by making an incision in the umbilicus.
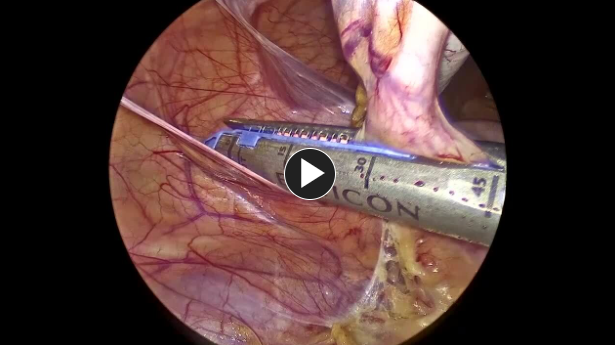
- Usually, a 12 mm trocar is used to enter the abdomen, and then lower pelvic 5 mm trocars are placed.
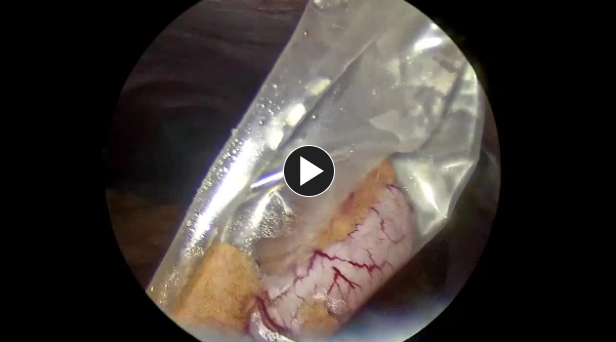
- Once completed, the appendix is placed in a specimen retrieval bag and removed through a 12 mm port.
- A drain is placed in the right lower quadrant if there are signs of perforation.
- The appendix is removed in the specimen retrieval bag through the 12 mm trocar site.
(Back to the top)
3. Closure
- A suture like a size 0 Vicryl™ Plus Antibacterial suture, is used to reapproximate the fascia of the umbilicus.
- The remaining trocars are removed. The wounds are closed using synthetic absorbable monofilament, such as Monocryl™ Plus Antibacterial suture, and a topical skin adhesive such as DERMABOND™ Mini Topical Skin Adhesive, or any appropriate dressing.
The patient is extubated, the Foley is removed, and the patient is taken to the recovery room.
Potential complications include but are not limited to:
Bleeding requiring reoperation
Note: If reoperation is necessary then an adjunctive hemostat such as SURGICEL SNoW™ or SURGICEL Powder™ might be a good option to control bleeding where primary methods (energy, staples, sutures, or clips) are ineffective or impractical.
- Surgical site infection (deep or superficial)
- Fecal fistula
- Conversion to open appendectomy
- Need for midline laparotomy
- Open wound
- Need for additional tests or procedures
Post-operative Patient Care
Typical recommendations for post-operative care may include, but are not limited to, any of the following:
- After completion of the surgical procedure, the patient is out of bed, ambulating, with appropriate pain control.
- Diet is advanced as tolerated, with plans for discharge on postoperative day 1 for uncomplicated appendicitis.
- Resumption of normal activity occurs within 1 day following the procedure; adequate analgesia allows safe return to daily duty.
- Discharge instructions consist of pain management, instructions on the future signs and symptoms indicating potential complications, and a follow-up office appointment.
- The postoperative outpatient office visit evaluates the patient's improved progression with a detailed history and physical examination, discussion of the final pathology, and evaluation of the surgical wound.
Additional resources
Access our on-demand Colorectal video library
Looking for more? Explore procedural videos and webinars from global experts
Stapling Academy
This program offers interactive learning about the science of stapling and novel stapler design technologies.

Energy Academy
This program offers concise learning to understand monopolar, bipolar, and ultrasonic energy modalities.