George Crawford, MD
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Procedure Overview
The gallbladder serves as a storage bin for bile, a digestive agent produced by the liver. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is minimally invasive surgical removal of a gallbladder.
INDICATIONS & OBJECTIVES:
- Bilary Colic
- Cholelithiasis (gallstones in the gallbladder, commonly due to high cholesterol)
- Choledocholithiasis (gallstones in the common bile duct)
- Cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder)
- Gallbladder Cancer
- Pancreatitis (Biliary)

Pre-operative Patient Care
Typical recommendations for pre-operative care may include, but are not limited to, any of the following:
- Abdominal ultrasound and liver function tests.
- HIDA\PIPIDA scan to evaluate for biliary dyskinesia.
- Nothing by mouth (NPO) for 8 hours before surgery.
- Cardiopulmonary evaluation as needed.
- Anesthesiology consultation as needed.
- Prophylactic antibiotics for patients with acute cholecystitis.
- Preoperative endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) for patients with clinical, laboratory, or radiographic evidence of choledocholithiasis. (Some surgeons with advanced laparoscopy experience may prefer laparoscopic common duct exploration.)
Prep & Patient Positioning
Common patient positioning:
- The patient is supine with the arms perpendicular to the body or tucked to the side.
The surgeon stands on the patient's left side, while the assistant stands on the patient's right.
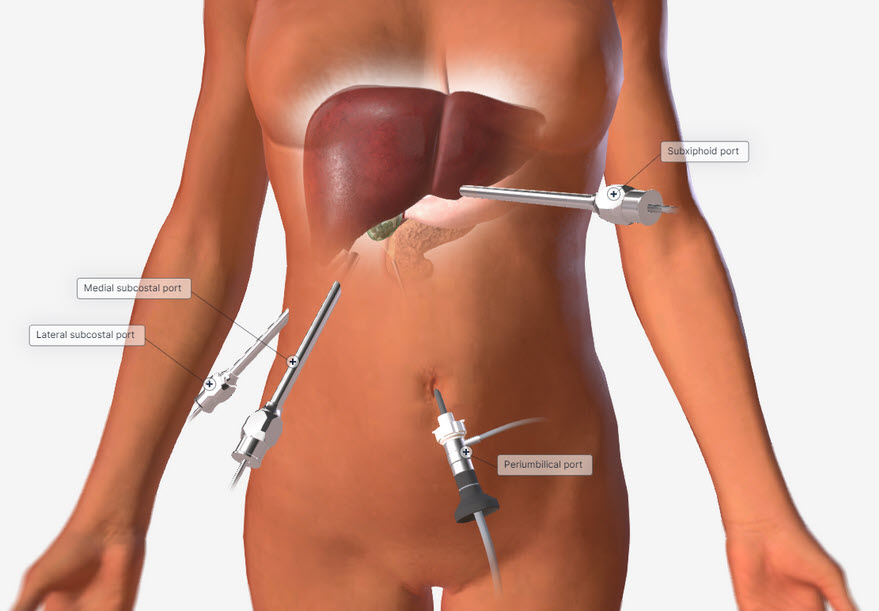
Common port placement
- Periumbilical/camera port
- Lateral subcostal
- Medial subcostal
- Subxiphoid port
Operative Steps
1. Access
- Access is generally obtained by making an incision in the umbilicus.
- Usually, a 12 mm port is placed through the umbilical incision under direct visualization.
- The abdomen is insufflated.
- Generally, a subxiphoid 5mm trocar and two right subcostal trocars are placed.
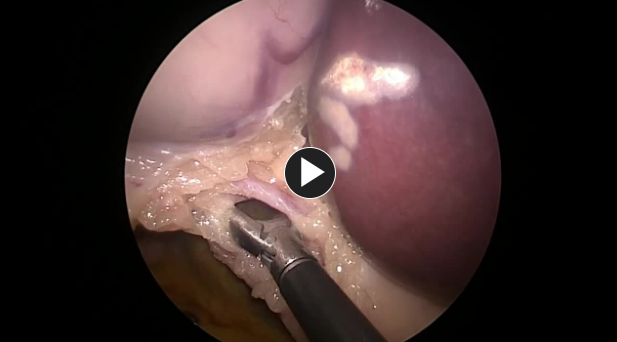
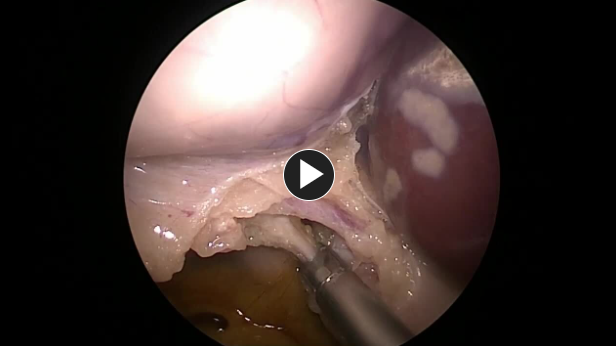
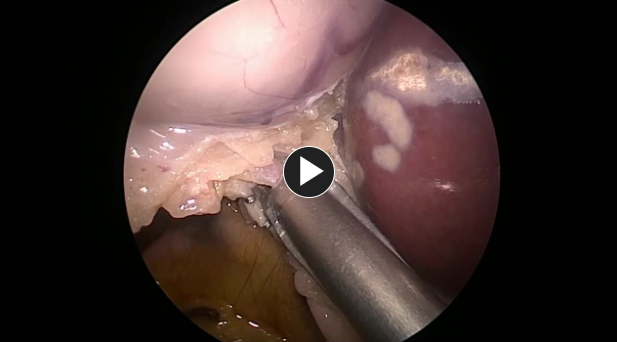
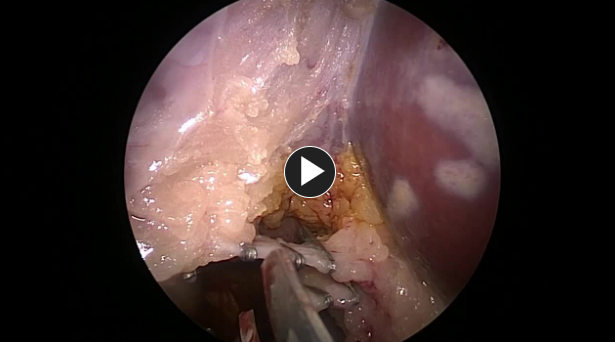
- Any adhesions to the gallbladder are taken down using electrocautery or ultrasonic shears.
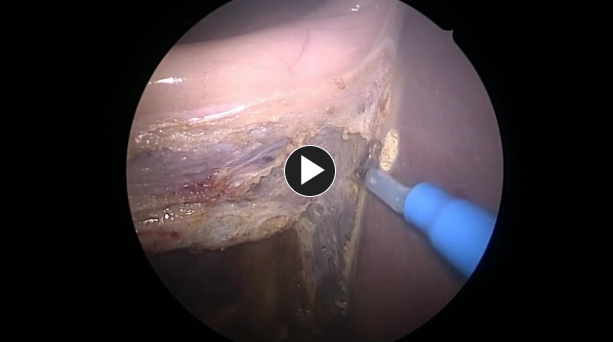
The gallbladder is removed from the gallbladder fossa using electrocautery or an ultrasonic energy device such as HARMONIC™ 1100.
Hemostasis is obtained while removing the gallbladder.
NOTE: Adjunctive hemostats such as SURGICEL SNoW™ or SURGICEL Powder™ may be used if the liver bed is oozing and where primary methods (energy, staples, sutures, or clips) are ineffective or impractical.
- The gallbladder is placed in an endoscopic specimen retrieval bag and removed through the 12 mm port.
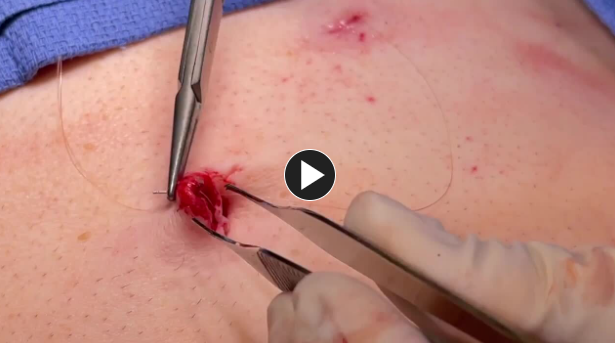
- The remaining trocars are removed. The wounds are closed using synthetic absorbable suture, such as Monocryl™ Plus Antibacterial suture, and a topical skin adhesive such as DERMABOND™ MINI™ Topical Skin Adhesive, or any appropriate dressing.
The patient is extubated and taken to the recovery room.
Post-operative Patient Care
Typical recommendations for post-operative care may include, but are not limited to, any of the following:
- Discharge home as this is usually an out-patient procedure.
- Follow-up with surgeon in 1-3 weeks.
- Pain Medication as prescribed.
- Nausea Medication if necessary.
- Instructions per protocol.
Additional resources
Access our on-demand Upper GI & Abdominal video library
Looking for more? Explore procedural videos and webinars from global experts

Energy Academy
This program offers concise learning to understand monopolar, bipolar, and ultrasonic energy modalities.